Hard disk drive (HDD) is commonly used in traditional computer configuration; however, solid state disk (SSD) emerges and tends to replace HDD gradually as the technology advances. So, which one is better, HDD or SSD? And what are the differences between them?
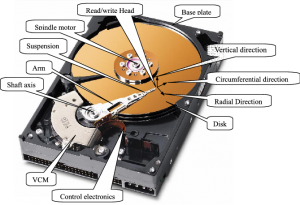
HDD, namely mechanical hard disk, consists of several components: Disc,
magnetic head, disc spindle and control motor, head controller, data converter, interface, and cache etc.
All HDD discs are installed on the same spindle and parallel to each other. There is a magnetic head which has a space smaller than the diameter of the hair with the disc on the storage surface of each disk. All heads are connected to a head controller, which controls the motion of each head. The heads can be positioned at specified locations of the disk for data read and write, as the heads are able to move along the radius of the disc, and the disc spins at a speed of several thousand revolutions per minute. As precision equipment, HDD must be completely sealed with dust as its formidable enemy.
SSD (Solid State Disk or Solid State Drive), also known as electronic hard disk or solid state electronic hard disk, is a hard drive consisting of control unit and solid state storage unit (DRAM or FLASH chip). SSD possesses identical interface specifications and definitions, function, and usage with HDD, and is consistent with the mechanical hard disk in the product shape and size.
Solid-state storage technology (SSD) generally has two types: one is flash memory base SSD using FLASH MEMORY as a storage medium. This is also the SSD type we commonly see, and what we use a lot such as U Disk, digital cameras and other electronic storage devices, and other flash disks carrying ATA, SCSI, and FC interface, are collectively known as FLASH drive; The other one is DDRRAM base SSD using DDRRAM as a storage medium. It follows the traditional design of disk drives with volume settings and management could be done by various file system tools of operating system, and provide the industrial standard PCI and FC interface used to connect to the host/server or storage network storage devices. It can be divided into two large sections: SSD drive and SSD disk array, and is true high-performance storage. Plus its service life is pretty long, and contains almost all the advantages that flash drives have or lack of, however, only one deficiency of it is that it needs power to ensure data security.
The best part of FLASH base SSD is its mobility, furthermore, the data protection is not subject to power source, which makes it adaptable in various environment, but the life span isn’t good enough. So the capacity of flash disk is generally very small, the ones with capacity above G level are counted as high capacity, till now, the largest flash disk has a 64G capacity. It is suitable for personal PC users, but there is no way to apply it to the enterprise’s storage system. As flash base SSD is equipped with quite high data security, plus its unparalleled advantages in noise and portability than hard disk, it is widely used in aerospace, military, finance, telecommunications, e-commerce and other departments. 
The most obvious advantage of DDRRAM Base SSD than HDD is the speed, for e.g., it takes 200 milliseconds to run a circle for a 15,000 RPM hard drive, while data on SSD is stored in semi-conductor memory, I/O (input/output) operations can be performed for any storage unit in any location within a millisecond. Therefore, on the most critical I/O performance metrics for many applications — IOPs (how many IO actions per second), SSD achieves 50 to 800 times the speed of the hard disk.