Secure Digital, abbreviated as SD, is a non-volatile memory card format used in portable storage devices. This format was then developed by SD Association into an industry standard to ensure its specifications and compatibility at the same time. It is widely used in portable devices because of its small size, fast data transmission and hot plug features and so on.
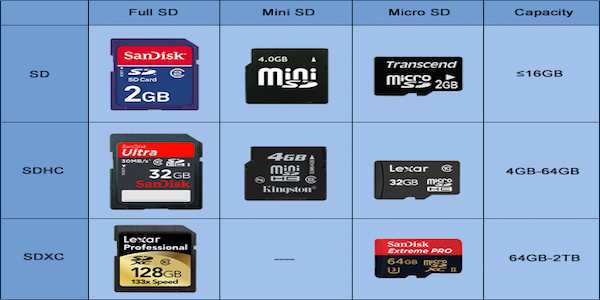
Four SD card families available in three different sizes:
The original Standard-Capacity (SDSC)
The High-Capacity (SDHC)
The eXtended-Capacity (SDXC)
The SDIO: combines input/output functions with data storage
Where to Use
The SD card is used in the following portable digital devices:
- store photos and video in digital cameras
- store photos and video in digital camcorders
- store all kinds of information in personal digital assistant (PDA)
- store photos, ringtones, music, short videos, etc in mobile phones
- used in multimedia player
SD Speed Class
SD card speed is customarily rated by its sequential read or write speed. The sequential performance aspect is the most relevant for storing and retrieving large files (relative to block sizes internal to the flash memory), such as images and multimedia. Small data (such as file names, sizes and timestamps) falls under the much lower speed limit of random access, which can be the limiting factor in some use cases.
The SD Association defines standard speed classes for SDHC/SDXC cards indicating minimum performance (minimum serial data writing speed). Both read and write speeds must exceed the specified value. The specification defines these classes in terms of performance curves that translate into the following minimum read-write performance levels on an empty card and suitability for different applications:
Class 0: including conditions lower than Class 2 and unmarked Speed Class;
Class 2: able to watch ordinary MPEG4 MPEG2 films, SDTV, digital camera shooting;
Class 4: able to play HDTV, support digital camera continuous captures and other functions;
Class 6: able to meet the requirement of Digital Single Lens Reflex continuous captures and professional equipment;
Class 10: Full hd TV recording and playback
UHS–I: Professional full hd TV live recording
UHS-II: for the future world
Important Cautions
SD card users often encounter some problems: sometimes the card is inserted several times, but the phone still cannot read it correctly. The specific analysis is as follows:
-
The SD card chip is not clean
Since some users do not protect the chip in an appropriate way, it is often covered with dust or oil, which causes the card reading to be abnormal.
Method: observe whether the metal area of the card is dim or whether there are spots.
Treatment: gently rub it with cotton cloth and some alcohol or water, and then re-insert it after drying.
-
The battery voltage is unstable
Since high quality card reading has a very strict requirement to the power supply, sometimes buying non-original battery is also easy to make card reading go wrong.
Method: in case of non-original battery, the standby condition is not ideal, and then the reason of battery should be suspected.
Treatment: change to the original battery and try again.
-
the slot is compressed
For some ultra-thin devices, the slot is cleverly designed. If you use some informal batteries, the thickness exceeds the requirement and the slot is squeezed, resulting in a bad card reading condition.
Method: change to the original battery and check
Treatment: use the original battery. And use something to hold the slot up.
-
The inside of the slot is rusted or bent
Because some phones support hot plug, frequent plug-and-unplug may cause the metal wires that read the card data in the slot to be curved or rusty.
Method: put the card slot towards the direction of the sun; observe whether the wire contact is at the same height. If not, then it may be the problem.
Treatment: try using a needle to adjust the wire.
-
SD virus
For some smart phones, SD may get infected through computers, which can also result in an inability to read the card properly.
Method: read the SD on computer and scan it.
Treatment: format the card on a computer or other low-end storage (such as camera, etc.), and for format on a computer, use a FAT format instead of a FAT32 format.
Hope the above cautions and suggestions can help you correctly deal with some common problems concerning with reading SD cards.