There I list 3 of differences between SSD and HHD in last article:
- Performance
- Different fundamental principles of read and write
- Different read and write speed.
Let us continue the last article ‘What are the Differences between SSD (Solid State Sisk) and HDD (Mechanical Hard Disk)?| Part 1‘ .
4. Data Security
We all know that the traditional hard disk reads and writes data through a magnetic head, so disk-head collisions are more likely to cause data damage during high speed rotation, plus transmission owperations also easily lead to loss of data. But solid-state drives have no discs, so as long as no deformation is caused by external extrusion for its chips, data can be preserved safely. So in terms of data security, there is a huge difference between SSD and HDD.
5. Write Cycles
SSD has a limit on write count, which means it has a service life. The SLC SSD is rated at 100,000 write cycles, while the general Entry-level solid-state drive which adopts MLC type has only 10,000 write counts. In theory, SSD will have a shorter life span, but the actual test says that SSD can be used for about five years on a MLC1 disk, which is also good enough.
Although the mechanical hard disk has no limit on the times for writing in, the general usage basically lasts for three or five years, so there is actually not much difference between the two.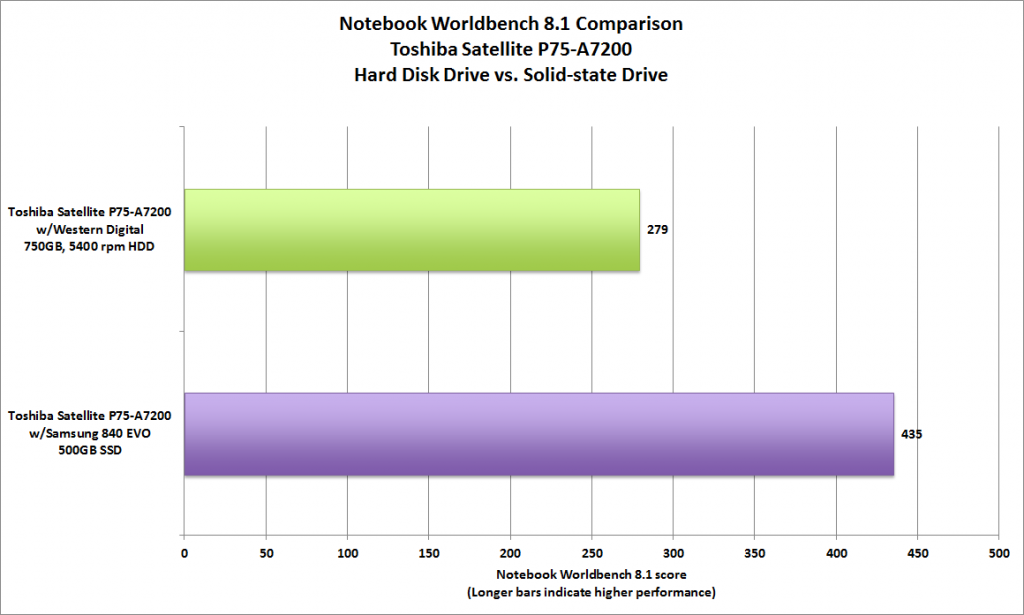
6. Data Recovery
If any data is deleted from SSD, it is not possible to recover it with the help of data recovery software or any other software, while traditional mechanical hard disk can be recovered by some professional data recovery software. This is also a drawback of SSD.
7. Differences in use between SSD and HDD
Differences in use between solid-state drives and ordinary hard drives are very big as well. Common hard disk, no matter what system is installed in, XP or Windows 7, is running the same way. While there exist a lot of SSD requirements, especially for the XP system. SSD support in XP system is not friendly. Using XP system will shorten the service life; XP does not optimize SSD, and will often make SSD read and write small files that SSD is not good at, which will not only slow the speed down, but also unnecessarily consume service life of hard disk. The most critical thing is that TRIM (garbage collection feature) of the hard disk in XP can’t be turned on, so the performance of solid-state drives will decay rapidly. In addition, if XP is installed, you must conduct 4K alignment for your solid-state drives, so that the performance could be improved.
In the case of installation, Windows 7 version system or above is recommended for SSD, and AHCI must be enabled, 4K alignment mush be done. You can download AS SSD Benchmark (SSD test software) to test whether or not the AHCI is enabled and 4K alignment is done.
8. Affordable price
Solid state drive has a great advantage in speed and security, and due to its latest technology, it’s much more expensive than traditional hard drive. SSD is now pricing at generally 2-3 times the price of traditional hard disk, but with the continuous development of Moore’s law, SSD’s NAND flash memory chip will be denser and denser, the storage capacity will be higher and higher, so the future price will also be lower and lower, we can predict that it’s imperative for solid-state hard disk to replace the traditional hard disk.
9. Noiseless
There is no mechanical motor and fan installed on solid-state drives, so the noise level is 0 dB at work, while mechanical hard drives are very noisy.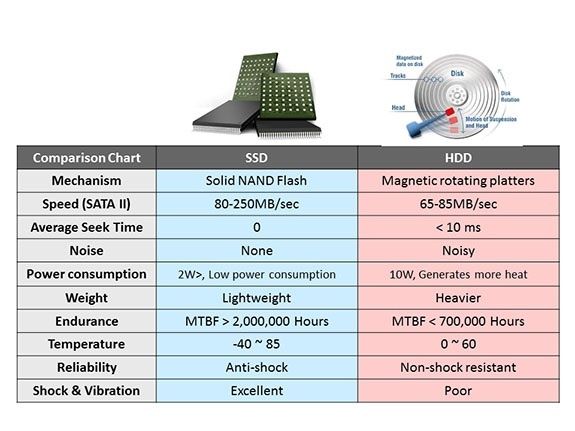
SSD and HDD are completely different in internal structures; SSD has only memory chip and circuit board, so the running noise almost equals zero. While HDD has a high speed motor inside, which generates noise and vibration at work, and if the vibration resonates with your case, the sound would be really disturbing. For the performance of current computer internal components, the performance of hard disk is the greatest pain in ass. If the hard disk performs insufficient, it will seriously affect the user experience even if other hardware configurations are high.
10. Power consumption
The maximum power consumption of HDD is about 5-10 w, and SSD is usually less than 3 w, low capacity flash base SSD has a lower energy consumption and heat output in working state, but high-end or large capacity product is going to be more energy intensive.



