USB is a standardize design connection of computer peripheral devices (including keyboards, pointing devices, digital cameras, printers, portable media players, disk drives and network adapters etc.) to personal computers, both to communicate and to supply electric power.
USB technology
One of the problem with USB is here was a lack of transfer speed for data from a peripheral to the host computer. Consider digital cameras for instance. As these devices became more commonplace, the need to transfer image data from the camera to the computer in a timely manner became more acute. The same can be said for other peripheral devices.
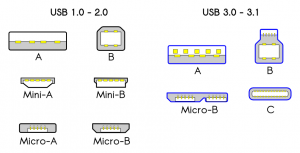 The USB 1.0 debut In 1996. While the original USB technology wasn’t particularly fast, it did offer some benefits. It allowed numerous types of peripherals to connect to a computer via the same type of connection. It replaced a variety of earlier interfaces, such as serial ports and parallel ports, as well as separate power chargers for portable devices , helping to lead to a more streamlined, functional device.
The USB 1.0 debut In 1996. While the original USB technology wasn’t particularly fast, it did offer some benefits. It allowed numerous types of peripherals to connect to a computer via the same type of connection. It replaced a variety of earlier interfaces, such as serial ports and parallel ports, as well as separate power chargers for portable devices , helping to lead to a more streamlined, functional device.
Debut of USB 2.0
The USB 2.0 release in April 2000. Compared to USB 1.0, the new generation offered numerous advantages to consumers. However, one of the most important was an increase in data transfer speeds. It adding a higher maximum signaling rate of 480 Mbit/s (High Speed or High Bandwidth), in addition to the USB 1.x Full Speed signaling rate of 12 Mbit/s. Due to bus access constraints, the effective throughput of the High Speed signaling rate is limited to 280 Mbit/s or 35 MB/s
| Release name | Release date | Maximum transfer rate | Note |
| USB 0.8 | December 1994 | Prerelease | |
| USB 0.9 | April 1995 | Prerelease | |
| USB 0.99 | August 1995 | Prerelease | |
| USB 1.0-RC | November 1995 | Release Candidate | |
| USB 1.0 | January 1996 | Low Speed (1.5 Mbit/s) | |
| USB 1.1 | August 1998 | Full Speed (12 Mbit/s) | |
| USB 2.0 | April 2000 | High Speed (480 Mbit/s) | |
| USB 3.0 | November 2008 | SuperSpeed (5 Gbit/s) | Also referred to as USB 3.1 Gen 1 by USB 3.1 standard |
| USB 3.1 | July 2013 | SuperSpeed+ (10 Gbit/s) | Also referred to as USB 3.1 Gen 2 by USB 3.1 standard |
| USB 3.2 | September 2017 | SuperSpeed+ (20 Gbit/s) | Also referred to as USB 3.1 Gen 3 by USB 3.1 standard |
| USB 2.0 | April 2000 | High Speed (480 Mbit/s) |

A USB flash drive, in diverse ways as a USB drive, USB stick, thumb drive, pen drive, jump drive, disk key, disk on key, flash-drive, memory stick or USB memory, is a data storage device that includes flash memory with an integrated USB interface, like SanDisk, Kingston etc.
USB flash drives supported natively by modern operating systems such as Windows, Linux, macOS. USB flash drives are typically removable and rewritable, and physically much smaller than an optical disc. Most weigh less than 30 grams and USB flash drives with anywhere from 8 to 256 GB are frequently sold, but less frequently 512 GB and 1 TB units. Storage capacities as large as 2 TB are planned, with steady improvements in size and price per capacity expected.



